Accounting is the process of recording financial transactions related to a business, with firms like Porte Brown being used to help with these finances. The accounting process can therefore include summarizing, analyzing, and reporting business transactions to oversight agencies, regulators, and, of course, tax collection entities. The financial statements used in accounting are concise summaries of financial transactions over an accounting period, and these statements summarize a company’s operations, financial position, and cash flows. Many companies find it much easier to hire in business accounting services to help out in this area because the stress of a business can make it difficult to keep on top of accounting. It is not only regular accounting that companies need to be using but also things like forensic accounting and digital forensics from companies like Eide Bailly to ensure everything is recorded and legal. Ultimately, regardless of the size of a business, accounting is a necessary process for decision making, cost planning, and measurement of economic performance. With this in mind, you can learn more about some of the different ways an accountant can support a business by reaching out to some of the most popular Accountants Perth has to offer. So, let us now discuss 5 important accounting terms that everyone should know.
Accruals
An accrual is an expense that is settled in the financial period following the one in which it was created. It is applicable when the accrual method of accounting is used as opposed to the cash accounting method which only takes account of expenses that are actually paid in a particular accounting period. The opposite of an accrual is a prepayment, where money is paid out in advance of the accounting period to which it relates. For example, rent that is paid 3 months in advance.
Assets
Assets can be fixed, current, tangible, or intangible. Fixed assets are those which are purchased by a business for its long-term use and not intended to be quickly converted back into cash. In other words, they are not liquid assets. Examples of fixed assets include buildings, vehicles, and equipment for use in a business rather than for resale. Conversely, it is expected that a business would convert its current assets back to cash within a year. For example, the stock that a business purchases which is to be resold at a profit. A tangible asset would be a fixed asset that you could see, such as a vehicle that is purchased for use in a business. Perhaps a van for deliveries. Whereas an intangible asset adds value to a business but cannot be physically seen. An example of an intangible asset would be the goodwill of a business. A well-known company name, or brand, will have value because of having an already established client base, and because of having built up a reputation of respect and reliability in the eyes of its target market. It is costly to set up a totally new brand. A lot of advertising and marketing, which comes at a cost, is required to become an established household name.
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to the reducing value of an asset over time. This relates to wear and tear. Particularly of vehicles, which are known to lose money the moment they are driven off the garage forecourt. So, in an accounting system, provision will be made for this loss. Not a loss until the vehicle is sold, but one that is taken account of as it can be used to set against income tax. There are, believe it not, five different methods of calculating depreciation: straight line method, reducing balance method, unit of production method, double declining balance method, and sum-of-the year’s Digits method. They all sound fascinating, but in terms of financial accounting, the top two are generally used. With these top two, it is a choice between taking the same amount of depreciation off each year the asset is depreciated or being more realistic and depreciating on a continually reducing balance. The amount claimed for depreciation over the longer term will be the same.
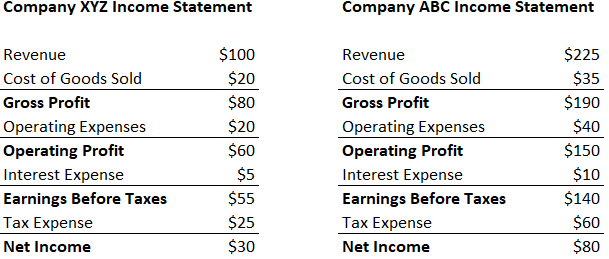
Net Profit
The net profit of a business is the profit that a business makes after all its expenses have been deducted. Gross profit only allows for the variable costs to be taken off, such as those that are directly involved in generating a business’s revenue. That is, those costs that directly generate sales, or result in the production of goods, relative to the amount of them that are sold or made. The net profit figure will be the one reported after all fixed costs, which are the same whatever a business’s productivity, have been deducted. Costs such as rent, insurance, heating and lighting of the building, and office wages.
VAT
VAT stands for Value Added Tax. It is collected by the UK government, and many other governments, as a tax on the sale of goods. Businesses will pay to their respective governments, the difference between the VAT on the goods that they have sold, minus that from the goods they have purchased. There will normally be monies to pay to HM Revenue and Customs due to the sale price of goods being higher than their purchase price. Although, if the company has made a large purchase of a fixed asset in a particular financial year, and quite correctly claimed the VAT back on that, because it was for business use, then there could be a refund of VAT due. The threshold for a business having to register for VAT as compulsory, for the 2020/21 tax period, is 85,000, although many businesses will elect to register for VAT anyway, so that they may claim VAT back on sundries and larger purchases bought for the business. Particularly where whole fleets of vehicles are purchased for use in the business. It is cost-effective to do so. The advantage of not registering for VAT is that businesses do not then have VAT to pass on to their customers, resulting in them being able to sell goods at a price that is maybe lower than their competitors.
So, a few accounting terms to consider here. There are, of course, many more to learn, if you are an accountant in training, or an entrepreneur or businessperson looking to keep tight control of your finances, by knowing something about your own figures. To know something about accountancy or finance will certainly help if you are trying to secure a start-up loan from a bank.

